Internal links works like a path that guide visitors to keep strolling thorugh your website, leading them on a journey to discover your website, other blogs and ideas.
Expert content writer, admin makes sure to design a clear marked paths for users to avoid any dead ends, Just like a garden with possibility to seeing a new flower on each steps.
Having lots of paths inside you website leads users to discover all the beautiful content on your site, which help in improving the user experience while boosting organic search rankings and website engagement.
How to Analyze the Impact of Internal Linking
Here are the basis key metrics to track you internal linking expertise include:
- Bounce Rate / Engaged Sessions: Understand how many users are interaction with your content. Track each sessions and bounce rate to get proper data to use it in future.
- Page Depth: How many clicks it would take for a user to go from you content page to homepage or vice versa. Understand this navigation a user fast from one page to another page is a best way to make user enagage with your site.
- Number of Internal Links (Backlinks) per page: Make sure you’re linking your own content very well. Having a good internal linking gives a good signal to google and help in ranking.
- Orphan pages: Find how many pages on your website have 0 internal linking from other pages or post on your site. You can find this easily in Google search console
- Pages per session: How many users are going from one page to another page on your site.
What are the Best Practices for Internal Linking
To improve your SEO performance and help in fast ranking you need to create an effective internal linking strategy is the key to guide users seamlessly through your site. Here are some guidelines to remember.
- Always audit your site internal links regularly. Optimize your links using info like site searches, dead clicks, headmaps, multipage sessions and user testing.
- Try to balance link quantity and distribution perfectly.
- Give anchor text that concise, specific and relevant.
- Use anchor/jump links to link to a specific section on a page.
- Understand how/when to nofollow, especially for sponsored links.
- Internal linking should be with most relevant and valuable content.
- Create a comprehensive library with the most important content for your users.
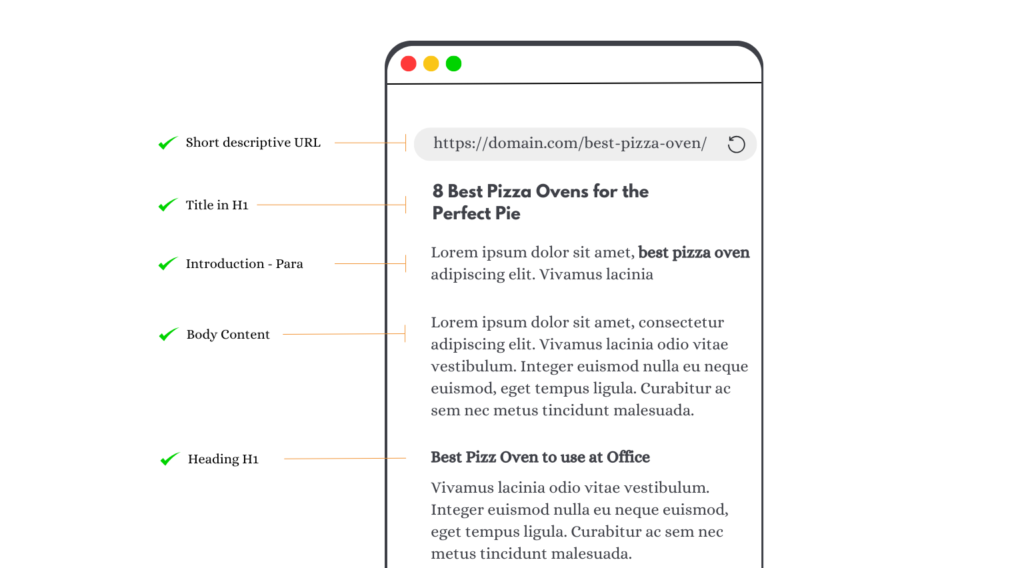
- Make your website well-organized, like organizing items in a store. Put things in folders that make sense, and use web addresses that are easy to understand. (Think of it like organizing a house – you want everything in the right room so people can find things easily)
Functional Copywriting for Anchor Link Text
Checklist: Internal Link Anchor Text
Good anchor text should meet the basic criteria of being clear, concise and helpful. It should like this:
- Make it clear what you can do there
- Easy to click on mobile
- It should look on mobile and desktop
- Different from the main content but should be relevant
- Add the right keywords
- Avoid focusing same keywords for different page/post
- Fit naturally in the content flow.
- Not overly optimized or repetitive
Great anchor text can also take it a step further and must:
- Send user to relevant next page for learning or buying funnel
- User should trust your internal linking
- Demonstrate more info is available on next page.
- Use exciting words that make people want to click.
Ask yourself: What would users do? (Think Like a User)
When making links on your website, test them yourself first and think: “Would visitors get what they expect when clicking this?” Be clear about where the link goes – like saying “see summer dresses” instead of just “click here.”
Examples of Effective Internal Linking
Think about some examples of link text from a user’s point of view and how to make it clearer, more specific, and useful.
- Instead of using: Click here
- Try: How to select and here’s your free report
- User Perspective: “Yeah I know this is a link. Why should I click it?”
- Instead of: Learn more
- Try: Add to cart, Claim yours now
- User Perspective: “Will I go to checkout next if I click this? But I’m not done shopping yet?”
- Instead of: Contact us
- Try: Get a free quote, Email Support
- User Perspective: “I need someone to come and help me with my problem”
More and more.
How to Audit Your Internal Links
You can use free tools to run a basis internal link audits, some tools you might already have used before like Google Search Console and Google Analytics.
Few SEO plugins are also available (WordPress Built Site) like All in One SEO and Detailed SEO, these 2 are great when you need quick check on any page.
Internal Link Audit Tools
- Google Search Console
- Google Analytics
- Screaming Frog
- Ahrefs
- Yoast , Ahrefs, and All in One SEO Plugins and etc.
How to Run Internal Link Audit
To do a basis Internal Link audit, start by finding broken links and orphan pages without any internal links in your site and fix to improve crawling. Once done with tha, you can work on optimizing links and link text.
- Find and fix broken links
- Check canonical links
- Export link title text
- Find and Fix orphan pages
- Filter for link text cannibalization
- Analyze link distribution
15 Common Internal Linking Practices to Rethink
Internal linking is a powerful way to improve SEO, guide user navigation, and establish content hierarchy on your website. However, some common internal linking practices can do more harm than good if not done thoughtfully. Here are 15 internal linking practices you might want to reconsider:
- Always Use the Exact Same Phrase for Links to a Page
- Issue: Repeating the same phrase can look spammy and overly SEO-focused.
- Solution: Vary your anchor text using top keywords and different phrasing to keep it natural. Link to relevant words even if they’re not exact keywords to avoid over-optimization.
- Link Any Relevant Words to a Page, Even if They Aren’t Exact Keywords
- Issue: Overuse of related links can cause keyword cannibalization and confuse Google about a page’s primary topic.
- Solution: Be selective with your linking. Use links where keywords are a direct match to the page’s primary focus.
- Include as Many Links as Possible on Each Page
- Issue: Google likely only crawls around 150 links per page, including navigation, so excessive links may not help.
- Solution: Place the most important links near the top of the page and streamline navigation to stay under the crawl cap.
- Avoid Links at the Top of the Page to Keep Users on the Page
- Issue: Users sometimes need quick redirection if they landed on the wrong page.
- Solution: Place helpful links or navigation near the top to guide users if needed, while clearly showing the purpose of each page.
- Don’t Link to the Same Page More Than Once
- Issue: Google doesn’t give extra weight to duplicate links, and they count toward the link crawl limit.
- Solution: Use multiple links if it enhances user experience or context, but avoid overuse.
- Hidden Links Are Still Counted by Google
- Issue: Hiding links can create a poor user experience and may be seen as deceptive.
- Solution: Only include links that are relevant to users and visible to them.
- Keep Link Text as Short as Possible
- Issue: Overly short anchor text can lack context and meaning.
- Solution: Use concise but descriptive link text that’s easy to click, especially on mobile.
- Open Internal Links in a New Tab to Boost Engagement
- Issue: Google Analytics won’t track engagement if users are in another tab, and it can be disorienting.
- Solution: Keep the experience consistent and let users choose where links open.
- Always Set External Links as Nofollow
- Issue: Linking to quality sites can build trust, and adding nofollow may imply lack of confidence in the source.
- Solution: Only nofollow links that don’t contribute value. Link to credible, relevant sources without nofollow.
- Avoid Linking to External Sites; Use Only Internal Links
- Issue: Relevant external links can enhance credibility and user trust.
- Solution: Don’t shy away from valuable external links that provide extra information or context.
- Don’t Start a Sentence with a Link
- Issue: Sometimes, the first words in a sentence are the most relevant for linking.
- Solution: Feel free to start a sentence with a link if it makes sense, just as you would with any other structure.
- Avoid Links in Headers to Avoid a Cluttered Look
- Issue: Users often pay close attention to headers, and header links can be highly visible.
- Solution: If heatmap data supports it, use links in headers strategically where users are likely to find them helpful.
- Avoid Linking in Certain Sections Due to Code Limitations
- Issue: Code limitations shouldn’t restrict user experience or SEO.
- Solution: Work with your tech team to understand code constraints and develop a flexible linking strategy.
- Internal Linking is the Responsibility of Only Certain Teams
- Issue: Restricting linking responsibilities may limit new linking opportunities.
- Solution: Educate the whole team on internal linking best practices to improve collaboration and maximize linking potential.
- Delay Adding Links to New Content Until Later
- Issue: Timely internal linking helps new pages get indexed faster and avoids additional auditing later.
- Solution: Establish a process to add links as soon as new content is published or updated.
Coming Future Trends in Internal linking
SEO tools continues to grow and getting advanced, In future we will see more automated suggestions for internal linking directly within CMS platforms while writing new content.
It could also be valuable to have comparison metrics with competitors—for example, an AI-powered link bot that crawls the SERPs for your page’s top keywords and tracks the number of internal backlinks competitors have for similar pages.
Ultimately, having a solid understanding of internal linking fundamentals will enable SEOs to fully leverage these advanced tools in the future.
Subscribe to our Newsletter: